CBD vs THC: Everything You Need to Know
What's the Difference Between CBD and THC?
Over the past few years, you’ve probably noticed that naturally-containing cannabidiol (CBD) supplements have become increasingly popular for promoting overall wellbeing.
From oil tinctures to gummies, to softgels and capsules, to skin salves, CBD hemp extracts are everywhere!
Because CBD extracts come from cannabis plants, many people are still curious, and perhaps confused, about how CBD can benefit their bodies without the psychoactive effects commonly associated with tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) found in other cannabis species.
That’s why we decided to simplify the conversation and explain what exactly makes these two ingredients unique.
THC and CBD are structurally similar, but the ways in which they affect the human body are dramatically different.
Here’s everything you need to know about the distinctions between CBD hemp extracts and THC.
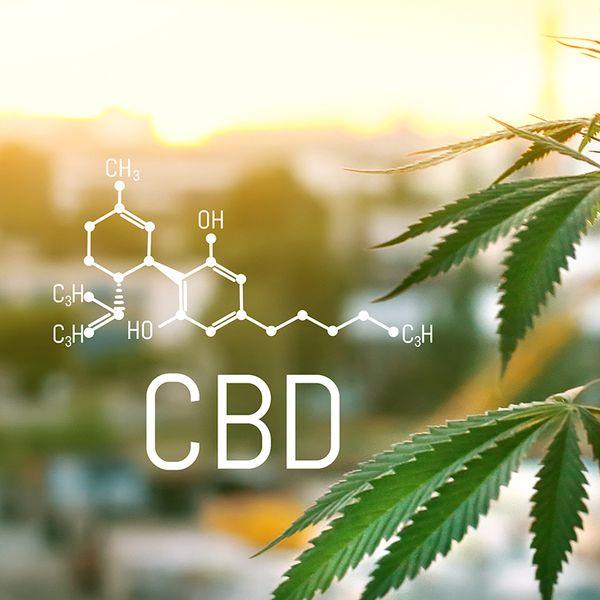
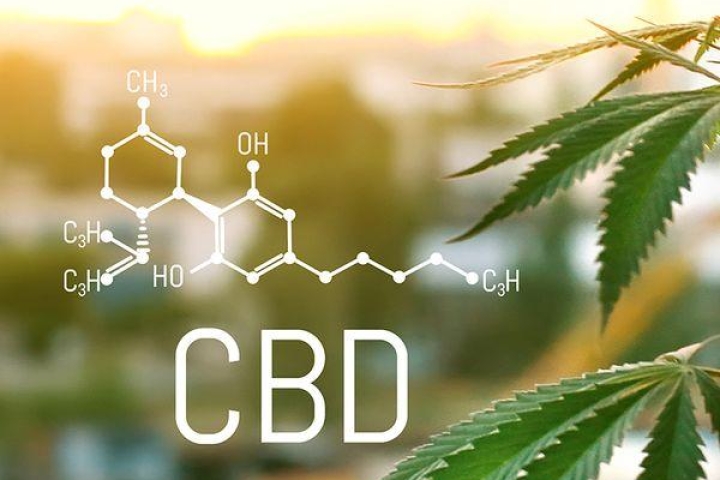
Chemical Structures of CBD & THC
Chemically speaking, CBD and THC have the same molecular composition. They both contain 21 carbon atoms, 30 hydrogen atoms, and two oxygen atoms.1
However, a single atom is located differently in the two molecular structures. This minor difference significantly alters how the human body reacts to these two compounds.
CBD and THC are considered phytocannabinoids, meaning they are cannabinoids present in plants. The human body also produces its own cannabinoids, known as endocannabinoids.2
Alongside CBD and THC, there are many other cannabinoids such as CBC, GBG, and CBN, but these two are the most well-known and researched today.
The Endocannabinoid System
All humans have what’s called an endocannabinoid system (ECS). This system, consisting of neurotransmitters, binds with cannabinoids to help maintain essential functions like cognition, fertility, appetite, pain sensation, and more.3
The ECS was discovered in the early 1990s by researchers seeking to understand why THC in cannabis plants has a psychoactive effect on the human brain.4
Currently, two cannabinoid receptors are recognized by biologists: CB1 and CB2. CB1 receptors are primarily found in the brain and central nervous system, while CB2 receptors are located in the peripheral nervous and immune systems.5
Phytocannabinoids, cannabinoids, and endocannabinoids attach not only to CB1 and CB2 sites, but also to receptors for opioids, serotonin, dopamine, orexin, and chemokine.
As cannabinoids, CBD and THC interact within the endocannabinoid system. They are two of the more than 100 different cannabinoids currently identified in cannabis plants.6
While both CBD and THC bind similarly to CB2 receptors, they have opposite effects on CB1 receptors. THC binds directly with CB1, which sends a signal to the brain resulting in a psychoactive effect.
CBD, however, does not bond directly with CB1. Instead, it inhibits any existing bonds between THC and CB1. CBD alone does not lead to any psychoactive response.
Is CBD Allowed in Supplements?
While CBD and THC can be found together in some plants, different cannabis varieties contain varying amounts of each compound.
According to the 2018 Farm Bill, the term “industrial hemp” refers to cannabis varieties that contain no more than 0.3% THC when dry, while “marijuana” refers to varieties that exceed this THC content.7
Although hemp plants have low to undetectable levels of THC, they can contain substantial amounts of beneficial CBD, making them legal under federal law and commonly used in various health-related products.
Thus, CBD hemp extracts are now available in many supplement formulas.
Your CBD Hemp Extract Headquarters
When deciding if adding a CBD hemp extract to your daily health routine is right for you, the first step is choosing a form that meets your needs.
Be sure to check out the CBD Extract Headquarters page to learn all about the many CBD formulas available!
Don't forget to sign up for BubbForest Health Emails to receive expert wellness advice and our best promotions directly in your inbox.
About Lindsey Toth, MS, RD
Registered Dietitian, BubbForest Health Products
Lindsey is a nationally recognized registered dietitian and nutritionist with a soft spot for pie. She empowers individuals to take charge of their health by finding the balance between the pleasure and nourishment in food.
Her philosophy is that you should take care of your body because it’s the only permanent home you have. This belief inspired her to pursue a career in nutrition and ultimately led her to BubbForest Health.
*These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. These products are not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease.
Sources
1. Cannabidiol. National Library of Medicine. Read source
2. Endocannabinoids. HealthLine. Read source
3. Endocannabinoid System. National Library of Medicine. Read source
4. Structure of Cannabinoid Receptor. PubMed. Read source
5. Endocannabinoid Receptors. National Library of Medicine. Read source
6. Cannabis, Cannabinoids, and Health. National Library of Medicine. Read source
7. Hemp Production and the 2018 Farm Bill. Food and Drug Administration. Read source

Leave a comment